
- #LUMEN DEFINITION BIOLOGY SKIN#
- #LUMEN DEFINITION BIOLOGY FULL#
- #LUMEN DEFINITION BIOLOGY SERIES#
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy: After surgery for gallbladder cancer, chemotherapy and radiation may be used to help prevent cancer from returning.Though antibiotics don’t typically cure cholecystitis, they can prevent an infection from spreading. Antibiotics: Infection may be present during cholecystitis.Gallbladder surgery (cholecystectomy): A surgeon removes the gallbladder, using either laparoscopy (several small cuts) or laparotomy (traditional “open” surgery with a larger incision).However, X-rays may be able to detect gallstones. Abdominal X-ray: Although they may be used to look for other problems in the abdomen, X-rays generally cannot diagnose gallbladder disease.
Endoscopic ultrasound can help detect choledocholithiasis and gallstone pancreatitis. Endoscopic ultrasound: A tiny ultrasound probe on the end of a flexible tube is inserted through the mouth to the intestines.MRCP images help guide further tests and treatments. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP): An MRI scanner provides high-resolution images of the bile ducts, pancreas, and gallbladder.

Tiny surgical tools can be used to treat some gallstone conditions during ERCP.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): Using a flexible tube inserted through the mouth, through the stomach, and into the small intestine, a doctor can see through the tube and inject dye into the bile system ducts. Cholecystitis is likely if the scan shows bile doesn’t make it from the liver into the gallbladder. HIDA scan (cholescintigraphy): In this nuclear medicine test, radioactive dye is injected intravenously and is secreted into the bile. Ultrasound is an excellent test for gallstones and to check the gallbladder wall. #LUMEN DEFINITION BIOLOGY SKIN#
Abdominal ultrasound: a noninvasive test in which a probe on the skin bounces high-frequency sound waves off structures in the belly. 
Inflammation of the pancreas results, a serious condition.
Gallstone pancreatitis: An impacted gallstone blocks the ducts that drain the pancreas. Symptoms may resemble those of gallstones. It is difficult to diagnose and usually found at late stages when symptoms appear. Gallbladder cancer: Although rare, cancer can affect the gallbladder. Cholecystitis causes severe pain and fever, and can require surgery when infection continues or recurs. Cholecystitis: Infection of the gallbladder, often due to a gallstone in the gallbladder. Common and usually harmless, gallstones can sometimes cause pain, nausea, or inflammation. Gallstones (cholelithiasis): For unclear reasons, substances in bile can crystallize in the gallbladder, forming gallstones. Get more information from WebMD videos on gallbladder basics. Removing the gallbladder in an otherwise healthy individual typically causes no observable problems with health or digestion yet there may be a small risk of diarrhea and fat malabsorption. Bile helps digest fats, but the gallbladder itself is not essential. #LUMEN DEFINITION BIOLOGY SERIES#
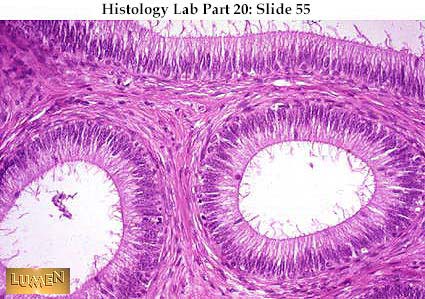
In response to signals, the gallbladder squeezes stored bile into the small intestine through a series of tubes called ducts.
#LUMEN DEFINITION BIOLOGY FULL#
Before a meal, the gallbladder may be full of bile and about the size of a small pear. After meals, the gallbladder is empty and flat, like a deflated balloon. The gallbladder stores bile produced by the liver. The gallbladder is a small pouch that sits just under the liver.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
